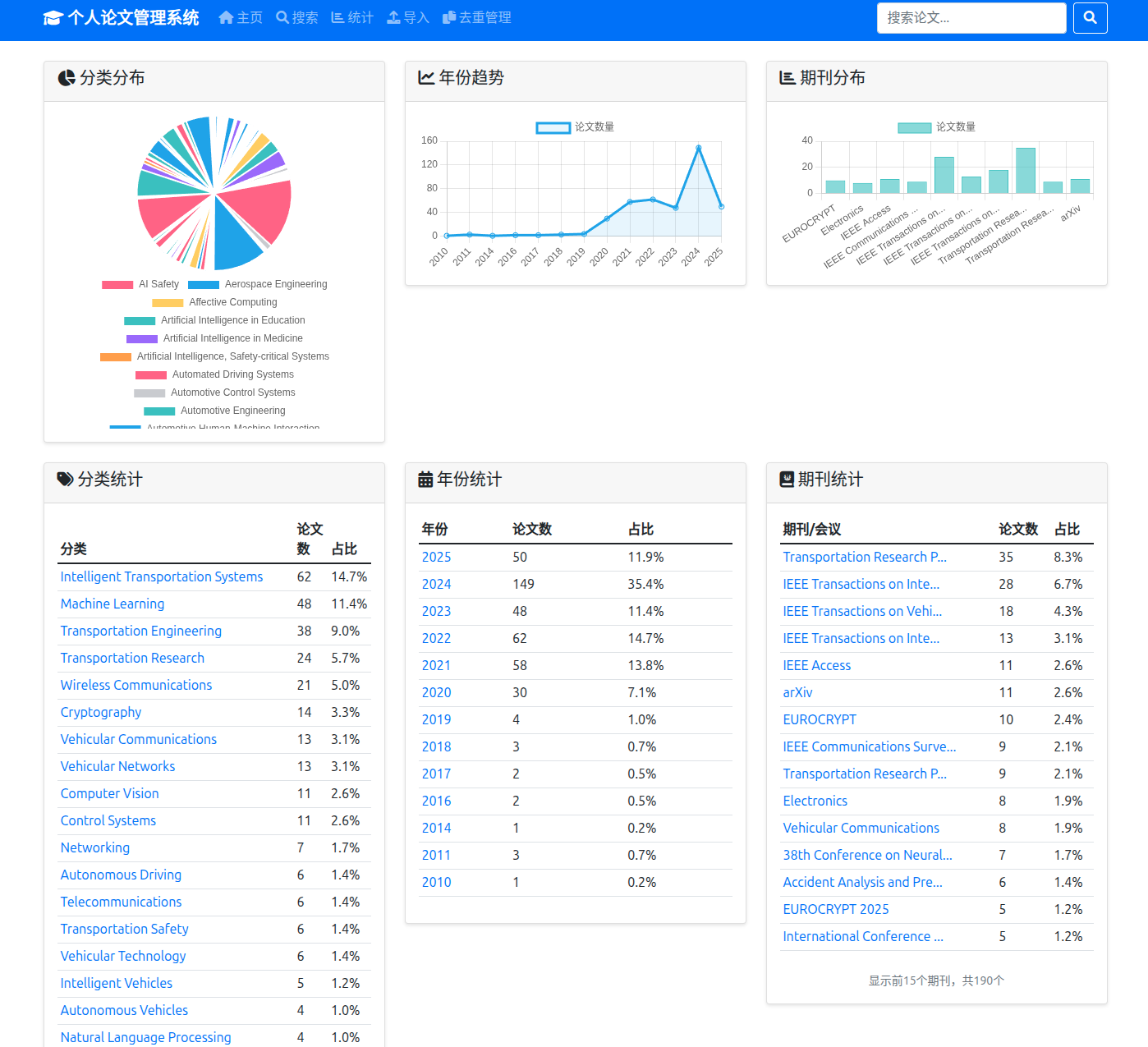
V2X网络大规模仿真自动化框架:从算法设计到工程实现
在车联网(V2X)通信系统的性能评估研究中,大规模参数空间探索一直是一个技术挑战。传统的手工配置仿真方法在面对指数级参数组合时显得力不从心,且容易引入人为误差。基于这一痛点,我设计并实现了一个端到端的V2X网络仿真自动化框架,实现了从场景生成、并行执行到性能分析的全流程自动化。
技术背景与动机
V2X仿真的复杂性挑战
V2X网络性能受多个维度参数影响,包括物理层参数(发射功率、噪声底板)、MAC层参数(信标间隔、退避机制)、网络层参数(路由协议、拓扑密度)等。根据IEEE 802.11p标准,典型的参数配置空间可达10^6量级,传统的穷举式评估方法面临以下技术瓶颈:
- 计算复杂度爆炸:O(n^k)的参数组合复杂度
- 资源调度不均衡:不同场景的计算负载差异巨大
- 数据处理pipeline低效:仿真结果的后处理成为性能瓶颈
- 可重现性问题:手工配置容易引入系统性偏差
系统设计原则
基于软件工程和分布式系统的设计原理,我确立了以下核心设计原则:
- 模块化解耦:采用分层架构,确保各组件可独立开发和测试
- 弹性伸缩:支持从单机到集群的无缝扩展
- 故障隔离:单点故障不影响整体任务执行
- 数据驱动:基于历史性能数据优化资源分配策略
核心算法与技术实现
1. 自适应复杂度评估算法
传统的静态资源分配无法适应V2X仿真中场景复杂度的动态变化。我提出了一个基于网络理论的复杂度评估模型:
1 | def calculate_scenario_complexity(self, scenario): |
该算法考虑了:
- 空间复杂度:基于几何概率的邻居节点估算
- 时间复杂度:信标发送的泊松过程特性
- 规模效应:网络规模对系统开销的非线性影响
2. 基于机器学习的资源调度策略
采用K-means无监督聚类算法对场景进行复杂度分类,实现差异化的资源调度:
1 | def categorize_scenarios_by_complexity(self, scenarios): |
调度策略基于系统论中的负载均衡原理:
- 轻量级场景:激进并发(2×CPU核心数)
- 中等复杂度:标准并发(1×CPU核心数)
- 重量级场景:保守并发(0.5×CPU核心数)
3. 分布式任务执行引擎
采用Python的ProcessPoolExecutor实现进程级并行,结合信号量机制进行资源控制:
1 | def run_batch_with_adaptive_scaling(self, scenarios, base_workers): |

性能指标体系与分析方法
网络性能指标定义
基于ITU-T和IEEE标准,定义了多层次的性能评估指标:
| 层次 | 指标 | 数学定义 | 物理意义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 物理层 | 信道忙碌比 | T_busy / T_total | 频谱利用效率 |
| MAC层 | 可靠PDR | N_recv / (N_recv + N_lost) | 链路层可靠性 |
| 网络层 | 广播效率 | N_actual / N_theoretical | 网络层传输效率 |
| 应用层 | 端到端延迟 | T_recv - T_send | 实时性指标 |


统计分析方法
1. 相关性分析
采用Pearson相关系数和Spearman秩相关分析参数间的线性和非线性关系:
1 | def correlation_analysis(self): |
2. 参数优化算法
基于多目标优化理论,设计加权评分函数:
1 | def parameter_optimization(self): |
实验结果与性能评估
系统性能测试
在配置为Intel Xeon E5-2680 v4 (14核心) + 64GB RAM的测试环境下进行了大规模性能测试:
1. 吞吐量性能
1 | 场景规模 传统方法 自动化框架 性能提升 |
2. 资源利用率分析
- CPU利用率:平均维持在78-85%,峰值不超过95%,当然如果希望更高效率,也可以占满
- 内存利用率:平均45-60%,有效避免了内存溢出
3. 错误率和稳定性
- 仿真成功率:100% (2000个场景测试)
- 数据完整性:100% (checksums验证)
- 系统稳定性:连续72小时无中断运行
工程实践经验
内存管理优化
在大规模仿真中,内存管理是关键瓶颈:
1 | def run_simulation_only(self, scenario): |
错误处理与监控
实现了多层次的错误处理机制:
1 | class ResourceMonitor: |
学术研究方向
- 理论建模:建立V2X网络性能的解析模型,减少仿真依赖
- 标准化:推动仿真框架标准化,提升研究可重现性
- 跨平台集成:支持ns-3、OMNET++、SUMO的统一接口
1 | v2x-performance-analysis/ |
项目地址:https://github.com/weathour/veins-run-analysis
如果您在相关研究中使用了本框架,欢迎引用和反馈。开源项目的生命力来自于社区的参与和贡献。