引言
在人工智能技术突飞猛进的今天,我们正处于一个独特的历史节点——后语言模型时代。大型语言模型的普及不仅改变了我们处理文本的方式,更从根本上重新定义了知识获取、整理和创作的范式。学术论文作为知识传播的核心载体,其海量的文本内容蕴含着丰富的结构化信息,等待着被更智能的方式解析和利用。
基于这一认知,我开发了PaperReader——一个集成了论文检索、智能解析、批量处理和知识管理的综合性学术工具系统。该系统的核心理念是:通过大型语言模型的深度文本理解能力,将传统的论文阅读从线性的文本消费转变为结构化的知识构建过程。
技术架构与系统设计
整体架构
PaperReader采用模块化的微服务架构,主要包含四个核心子系统:
- 论文管理系统 (
paper-management-system):Web界面的核心管理平台 - PDF-JSON检查器 (
pdf-json-checker):文件同步和数据验证工具 - PDF笔记生成器 (
pdf-note-generator):基于LLM的智能内容提取 - 浏览器扩展 (
browser_extension):便捷的数据采集工具
技术栈选择
系统基于以下技术栈构建:
- 后端框架:Flask + SQLite,保证轻量级部署和高效查询
- 前端技术:响应式HTML5/CSS3/JavaScript,确保跨平台兼容性
- 数据处理:Python生态(Pandas, jieba),支持多语言文本处理
- 智能匹配:基于
difflib.SequenceMatcher的相似度算法
核心创新:基于LLM的论文结构化解析
提示词工程的设计哲学
在后语言模型时代,提示词工程成为了连接人类意图与机器理解的关键桥梁。我在设计论文解析提示词时,遵循了以下原则:
- 结构化输出:严格的JSON格式要求,确保数据的机器可读性
- 多维度分析:不仅提取基础元数据,更深入挖掘论文的学术价值
- 学术规范性:符合学术界的引用和分类标准
核心提示词设计
系统使用的核心提示词如下:
1 | Please extract key information from the following academic paper and provide a detailed structured analysis, outputting only in strict JSON format (do not include any additional explanatory text): |
提示词设计的学术考量
这个提示词的设计体现了现代学术研究的多层次需求:
- 基础信息提取:标题、作者、期刊等元数据的准确识别
- 内容理解:摘要、方法论、结论的精确提取
- 深度分析:背景动机、概念框架、论证逻辑等高阶认知内容
- 学术话语分析:论文在学科话语体系中的定位和修辞策略
智能匹配算法:解决论文去重难题
多策略匹配机制
传统的文献管理往往面临重复论文识别困难的问题。PaperReader实现了基于多策略的智能匹配算法:
1 | def search_papers(self, query: Dict) -> List[Dict]: |
相似度计算的技术实现
系统采用SequenceMatcher进行文本相似度计算,并结合权重机制:
- 标题相似度权重:70%
- 作者相似度权重:30%
这种加权方式平衡了论文识别的准确性和召回率。
用户体验设计:从研究者视角出发
Web界面的功能模块
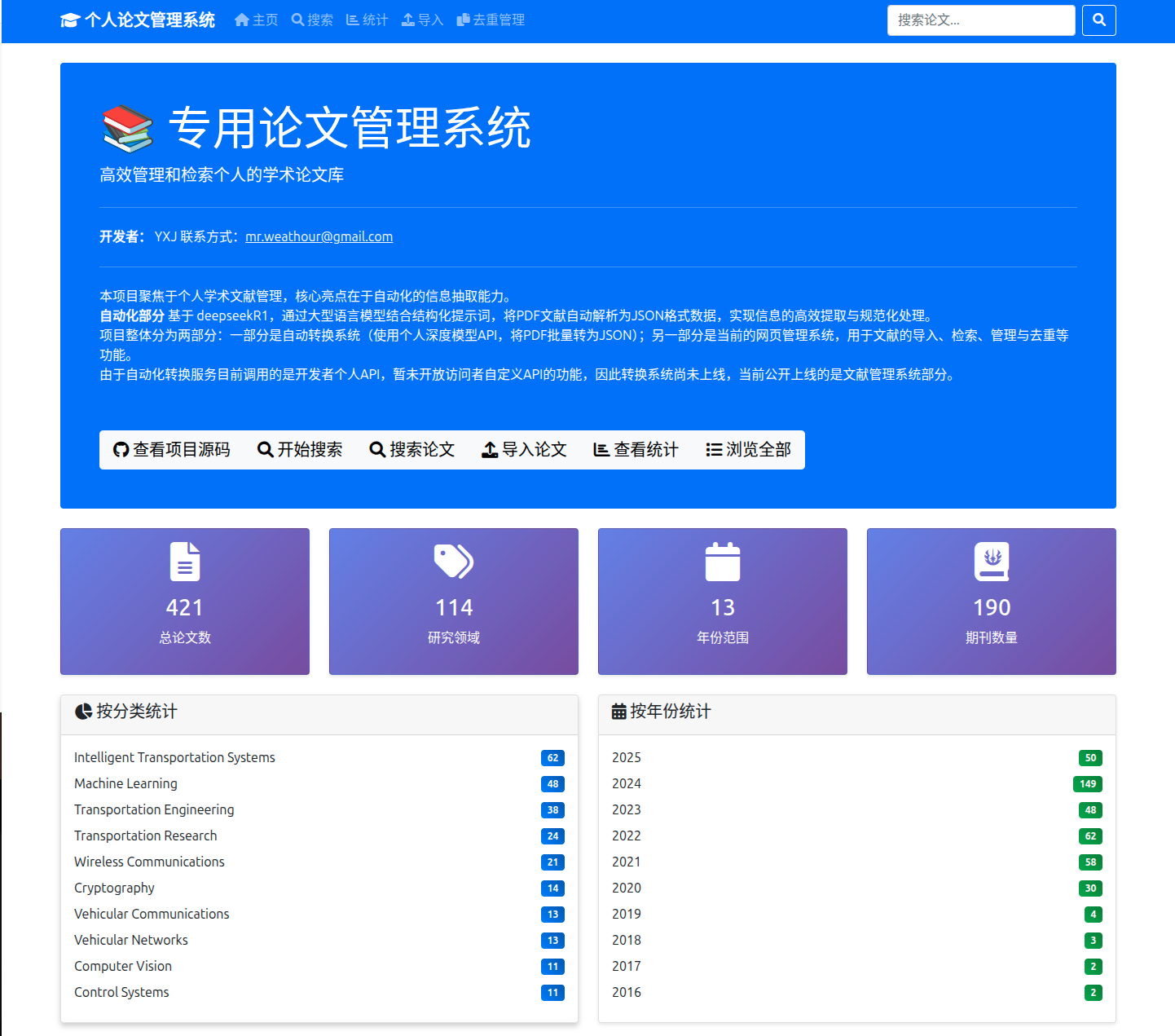
系统提供了完整的Web管理界面,主要包含:
- 搜索与浏览:多维度检索,支持按作者、期刊、年份筛选
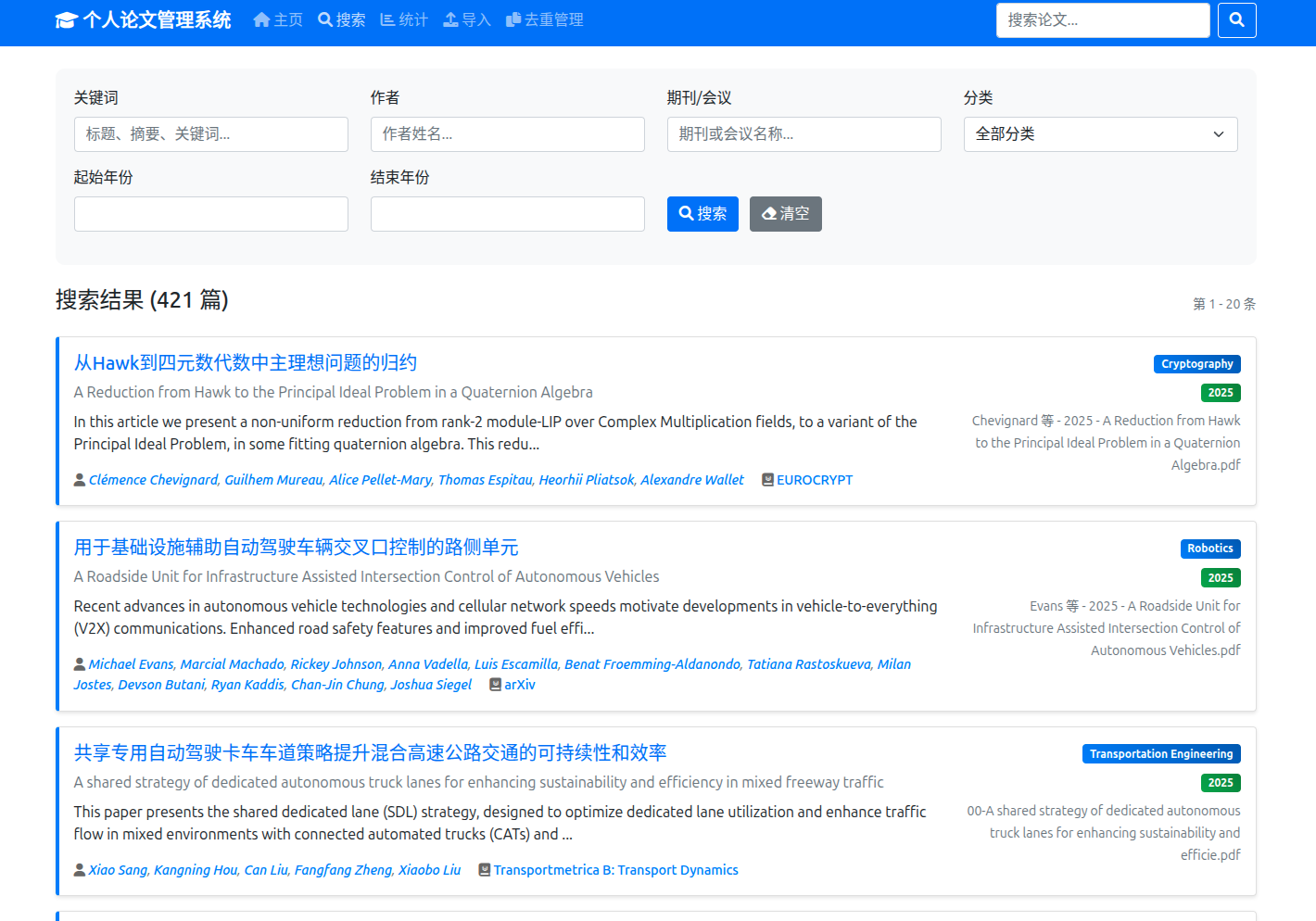
- 论文详情:结构化展示解析结果,支持PDF在线预览
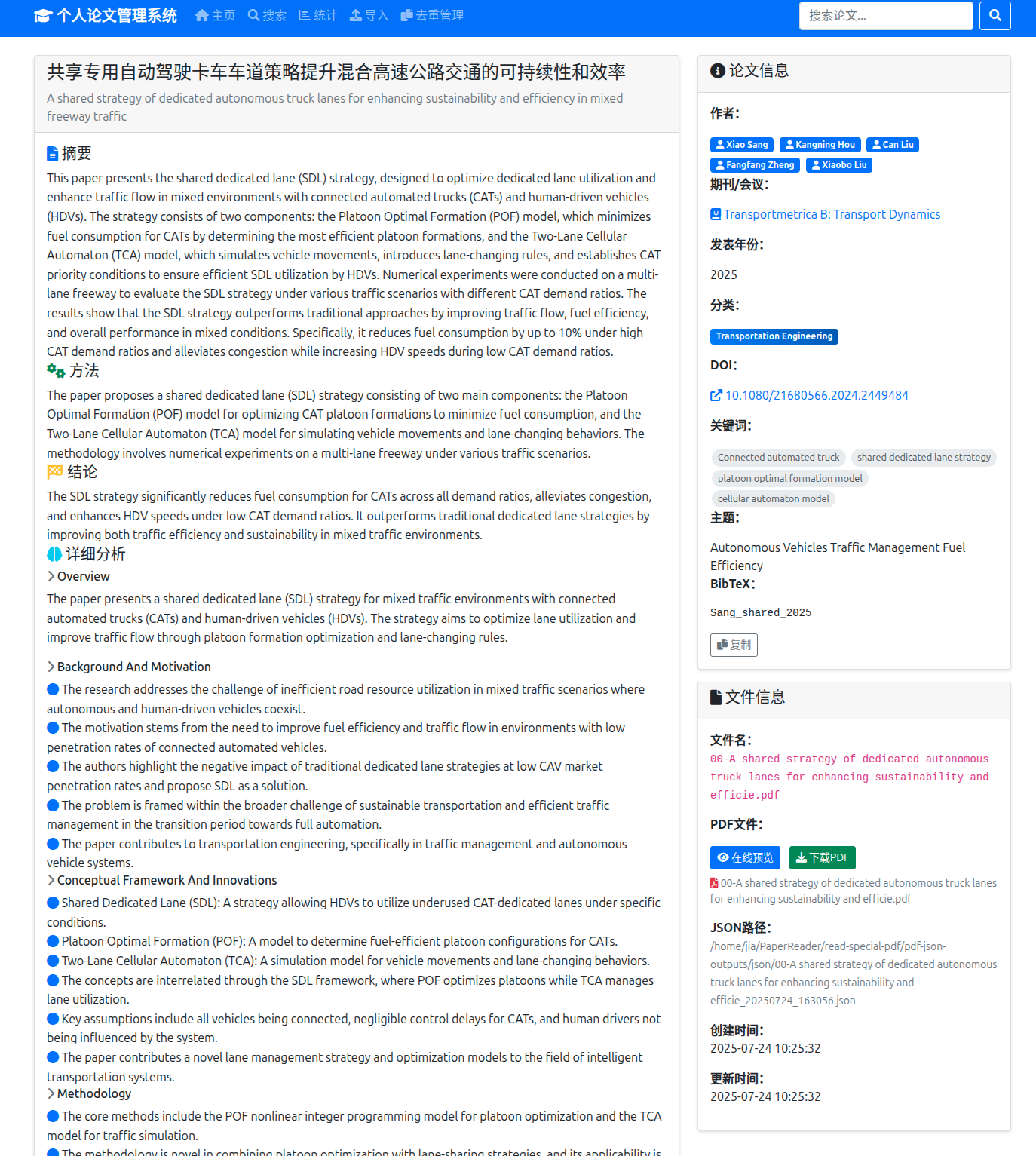
- 数据管理:批量导入、去重处理、统计分析
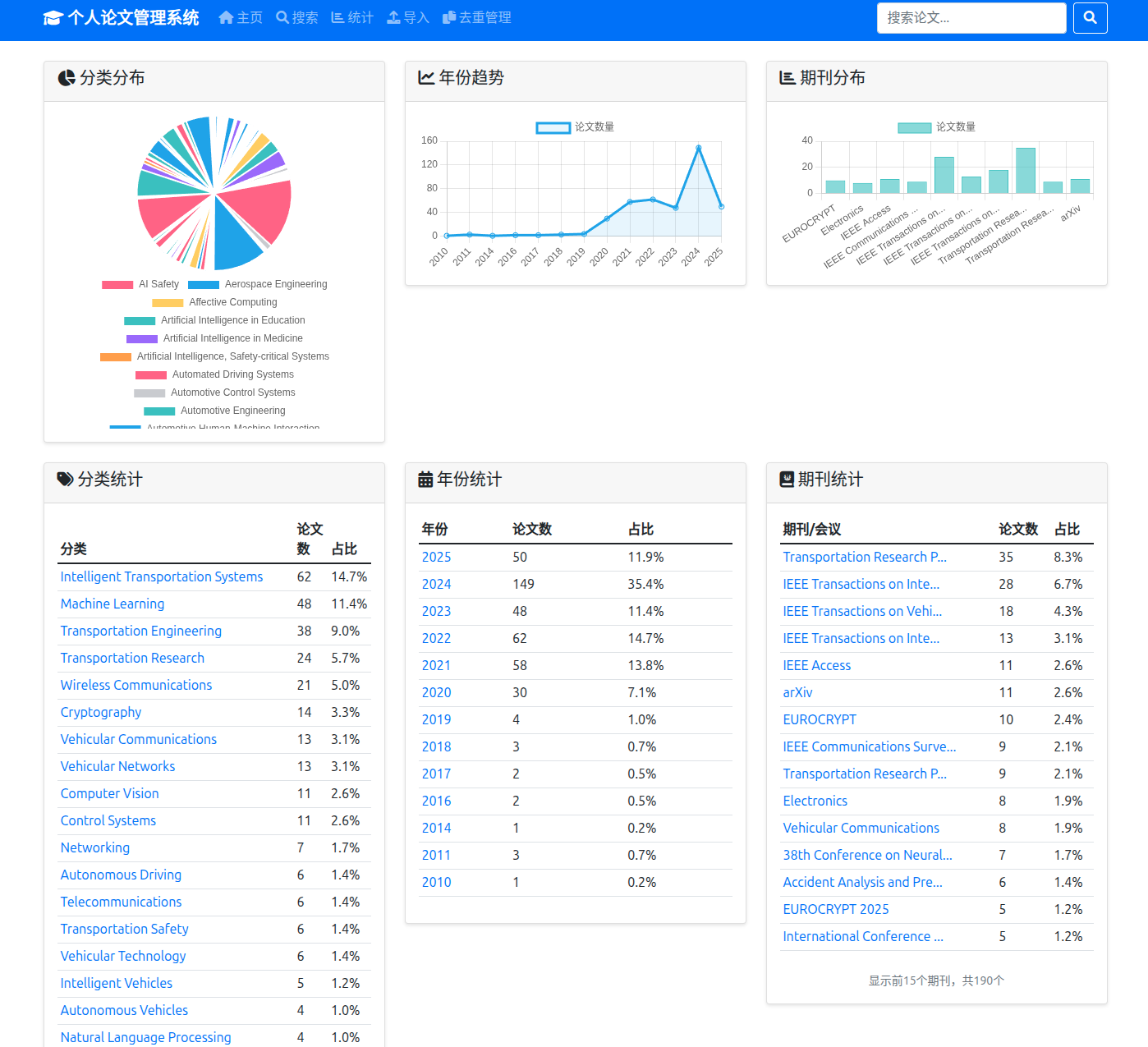
- 系统监控:导入状态、数据质量报告
- pdf分析:批量的pdf转json模块
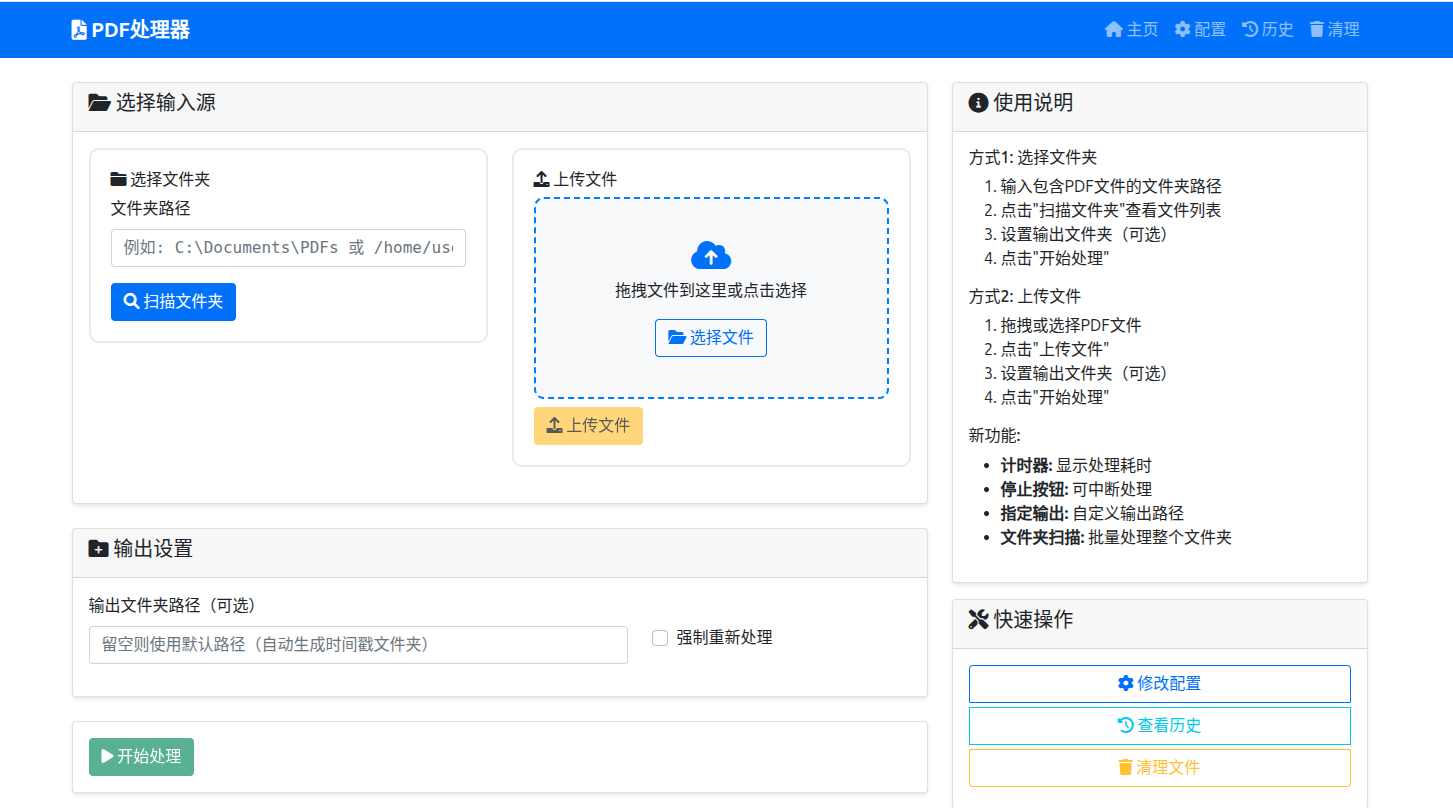
浏览器扩展的便捷性
开发的Chrome扩展实现了:
- 一键捕获论文信息
- 实时查重检测
- 与主系统的数据同步
对学术创作的促进作用
重新定义论文阅读
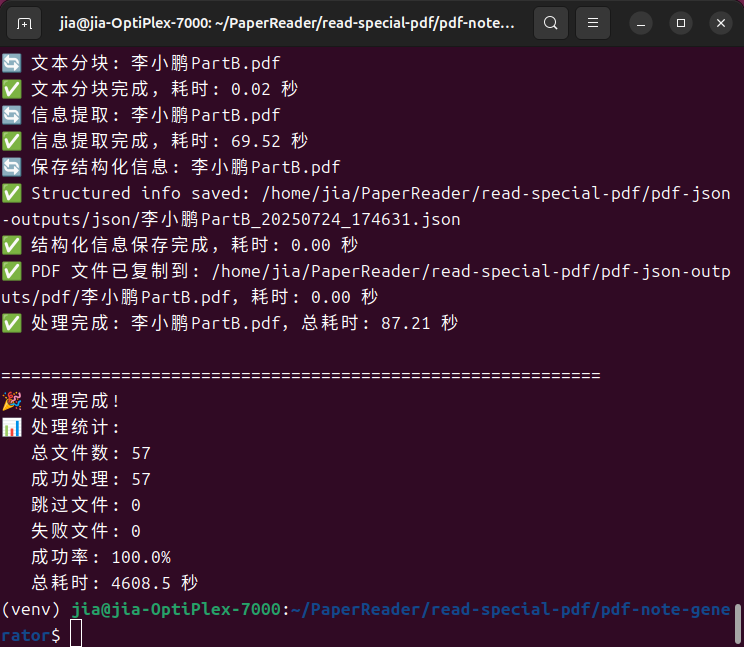
传统的论文阅读是线性的、时间密集的过程。通过LLM的结构化解析,研究者可以:
- 快速理解核心观点:通过结构化摘要直接把握论文要点
- 识别研究空白:通过批量分析发现研究趋势和空白领域
- 构建知识网络:通过概念框架分析建立领域知识图谱
促进创新性思维
系统的深度分析功能特别有助于:
- 批判性思维培养:通过”论证与逻辑”分析识别推理漏洞
- 跨学科视野拓展:通过”学术话语分析”理解不同学科的研究范式
- 研究方法学习:通过”方法论”分析掌握前沿研究技术
技术挑战与解决方案
数据质量保证
论文PDF的文本提取质量直接影响解析效果。系统通过以下方式保证数据质量:
- 多重验证:JSON格式验证、字段完整性检查
- 异常处理:容错机制处理OCR错误和格式异常
- 人工审核:提供Web界面进行数据校正
性能优化
面对大规模论文数据,系统采用了:
- 数据库索引优化:基于标题、作者、年份建立复合索引
- 分页查询:避免大结果集的内存占用
- 缓存机制:常用查询结果的内存缓存
未来发展方向
技术发展路线
- 多模态支持:整合图表、公式的理解能力
- 知识图谱构建:基于论文内容自动构建领域知识图谱
- 个性化推荐:基于阅读历史的智能推荐系统
- 协作功能:支持团队共享和协作批注
结语
PaperReader的开发实践表明,在后语言模型时代,学术工具的价值不再仅仅是信息的存储和检索,而是知识的理解、转化和创新。通过将大型语言模型的认知能力与传统的信息管理技术相结合,我们可以构建出真正促进学术创作的智能化工具。
这个系统的意义不仅在于提高了论文管理的效率,更在于它为研究者提供了一种全新的知识获取和创作模式。在信息爆炸的学术环境中,如何快速而深入地理解前沿研究,如何从海量文献中发现创新机会,将成为决定研究者学术生涯成功的关键因素。
项目代码已开源于GitHub,欢迎学术界同仁使用、改进和扩展。让我们共同探索人工智能时代的学术研究新范式。
项目地址: https://github.com/weathour/read-special-pdf
技术交流: 欢迎通过GitHub Issues进行技术讨论和问题反馈